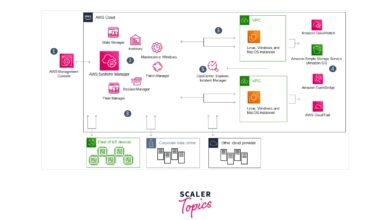
System Development: 7 Ultimate Secrets for Success
System development isn’t just about coding—it’s about creating smart, scalable solutions that power modern businesses. Whether you’re building software, automating workflows, or designing enterprise platforms, understanding the full lifecycle is key to delivering real value.
What Is System Development and Why It Matters

At its core, system development refers to the structured process of designing, building, testing, and deploying information systems to meet specific organizational needs. It’s the backbone of digital transformation across industries—from healthcare to finance, education to logistics.
The Evolution of System Development
System development has evolved dramatically since the mid-20th century. Early systems were monolithic, built on mainframes with rigid architectures. Today, we’re in an era of agility, cloud computing, and AI integration.
- 1950s–1970s: Procedural programming and batch processing dominated.
- 1980s–1990s: Structured methodologies like Waterfall emerged.
- 2000s: Object-oriented design and early agile practices took hold.
- 2010s–Present: DevOps, microservices, and continuous delivery define modern system development.
“The best systems aren’t built in a day—they evolve through iteration, feedback, and relentless improvement.” — Martin Fowler, Chief Scientist at ThoughtWorks
Key Components of a Development System
A successful system development lifecycle (SDLC) integrates several critical components:
- Requirements Gathering: Understanding what users and stakeholders need.
- Design Architecture: Creating blueprints for data flow, UI, and backend logic.
- Development & Coding: Writing clean, maintainable code using appropriate languages and frameworks.
- Testing & QA: Ensuring functionality, security, and performance meet standards.
- Deployment & Maintenance: Rolling out the system and providing ongoing support.
Each phase feeds into the next, forming a cohesive pipeline that minimizes risk and maximizes efficiency.
The 7 Phases of System Development Lifecycle (SDLC)
The System Development Lifecycle (SDLC) is a proven framework used to guide the creation of high-quality software systems. It ensures projects are delivered on time, within budget, and aligned with user expectations.
1. Planning and Feasibility Study
This initial phase determines whether a proposed system is technically, economically, and operationally feasible. Teams assess costs, timelines, resource availability, and potential risks.
- Conduct stakeholder interviews to identify goals.
- Evaluate existing systems for integration opportunities.
- Perform cost-benefit analysis to justify investment.
A well-documented feasibility report can prevent costly missteps later in the project.
2. Requirements Analysis
This stage focuses on gathering detailed functional and non-functional requirements. Functional requirements describe what the system should do (e.g., user login, data export), while non-functional ones cover performance, scalability, and security.
- Use techniques like user stories, use cases, and wireframing.
- Engage end-users early to avoid scope creep.
- Document requirements in a Software Requirements Specification (SRS).
According to the Standish Group’s CHAOS Report, poor requirements management is a leading cause of project failure.
3. System Design
Once requirements are clear, the design phase translates them into technical specifications. This includes both high-level architecture (like choosing between monolithic vs. microservices) and low-level details (database schemas, API contracts).
- Create data flow diagrams (DFDs) and entity-relationship diagrams (ERDs).
- Define technology stack: programming languages, frameworks, databases.
- Ensure compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO/IEC 25010).
Good design reduces technical debt and makes future enhancements easier.
4. Implementation (Coding)
This is where developers write the actual code. The implementation phase turns design documents into working software modules.
- Follow coding standards and version control practices (e.g., Git).
- Use integrated development environments (IDEs) like Visual Studio Code or IntelliJ IDEA.
- Adopt test-driven development (TDD) to improve code quality.
Collaboration tools like GitHub and Jira help teams manage tasks and track progress efficiently. For more on best coding practices, check out GitHub’s official documentation.
5. Testing
No system development process is complete without rigorous testing. This phase identifies bugs, validates functionality, and ensures the system behaves as expected under various conditions.
- Unit testing: Verify individual components.
- Integration testing: Check how modules interact.
- System testing: Evaluate the complete system.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Confirm it meets business needs.
Automated testing tools like Selenium, JUnit, and Postman streamline this process and reduce human error.
6. Deployment
After successful testing, the system is deployed to production. Deployment strategies vary based on risk tolerance and system complexity.
- Big Bang: Full rollout at once (high risk).
- Phased: Gradual release by module or department.
- Parallel: Old and new systems run simultaneously.
- Blue-Green: Two identical environments; switch traffic after testing.
Modern CI/CD pipelines automate deployment, reducing downtime and increasing reliability. Learn more about deployment best practices at Atlassian’s guide to Continuous Delivery.
7. Maintenance and Evaluation
Even after launch, system development isn’t over. Maintenance ensures the system remains functional, secure, and up-to-date.
- Corrective: Fix bugs discovered post-deployment.
- Adaptive: Modify the system for new environments (e.g., OS updates).
- Perfective: Improve performance or usability.
- Preventive: Optimize code to prevent future issues.
Regular evaluation helps organizations measure ROI and plan for future upgrades.
Popular System Development Methodologies Compared
Choosing the right methodology is crucial for project success. Different approaches suit different types of system development, team sizes, and business goals.
Waterfall Model: Linear and Predictable
The Waterfall model follows a sequential approach—each phase must be completed before the next begins. It’s ideal for projects with stable, well-defined requirements.
- Pros: Clear milestones, easy to manage, documentation-heavy.
- Cons: Inflexible to change, late testing, high risk if requirements shift.
Commonly used in government, aerospace, and regulated industries where compliance is critical.
Agile: Flexible and Iterative
Agile emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback, and small, rapid releases. It’s one of the most popular approaches in modern system development.
- Works in sprints (typically 2–4 weeks).
- Encourages daily stand-ups and retrospectives.
- Uses frameworks like Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP).
According to the State of Agile Report, over 70% of organizations use Agile to improve delivery speed and responsiveness.
DevOps: Bridging Development and Operations
DevOps extends Agile by integrating development and IT operations. It enables faster, more reliable deployments through automation and continuous feedback loops.
- Automates build, test, and deployment processes.
- Uses monitoring tools like Prometheus and Grafana.
- Promotes a culture of shared responsibility.
Companies like Amazon and Netflix rely on DevOps to deploy thousands of times per day.
Tools and Technologies Powering Modern System Development
Today’s system development landscape is rich with tools that enhance productivity, collaboration, and quality assurance.
Integrated Development Environments (IDEs)
IDEs provide a comprehensive workspace for coding, debugging, and testing.
- Visual Studio Code: Lightweight, extensible, supports multiple languages.
- IntelliJ IDEA: Preferred for Java and JVM-based development.
- PyCharm: Ideal for Python developers.
These tools often include AI-powered assistants like GitHub Copilot to suggest code snippets.
Version Control Systems
Version control is essential for tracking changes and enabling team collaboration.
- Git is the de facto standard, used by over 90% of developers.
- Platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket offer hosting and CI/CD integration.
- Branching strategies (e.g., Git Flow) help manage feature development and releases.
Learn more about Git best practices at the official Git documentation.
Project Management & Collaboration Tools
Effective communication is vital in system development. These tools keep teams aligned.
- Jira: Tracks issues, sprints, and bugs.
- Trello: Visual Kanban boards for task management.
- Slack: Real-time messaging and integrations.
They integrate seamlessly with development workflows, reducing silos between departments.
Common Challenges in System Development and How to Overcome Them
Despite advances in tools and methodologies, system development still faces significant hurdles.
Scope Creep and Requirement Volatility
One of the biggest threats to project success is uncontrolled changes in requirements. Stakeholders often request new features mid-project, leading to delays and budget overruns.
- Solution: Implement a formal change control process.
- Use Agile sprints to accommodate evolving needs incrementally.
- Set clear boundaries in the SRS document.
Regular stakeholder reviews help align expectations and reduce surprises.
Poor Communication Between Teams
When developers, testers, and business analysts don’t communicate effectively, misunderstandings arise, leading to flawed implementations.
- Solution: Hold daily stand-up meetings.
- Use collaborative tools like Confluence for documentation.
- Encourage cross-functional team structures.
DevOps culture promotes transparency and shared ownership, reducing communication gaps.
Technical Debt Accumulation
Technical debt refers to shortcuts taken during development that compromise long-term code quality. While sometimes necessary, unchecked debt slows future development.
- Solution: Refactor code regularly.
- Adopt coding standards and peer reviews.
- Allocate time in sprints for technical improvements.
“Technical debt is like financial debt—it’s okay if managed, but dangerous if ignored.” — Ward Cunningham, inventor of the wiki
The Role of AI and Automation in System Development
Artificial Intelligence is transforming how we approach system development, making processes faster, smarter, and more efficient.
AI-Powered Code Generation
Tools like GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer use machine learning to suggest entire lines or functions of code based on natural language prompts.
- Reduces boilerplate coding time.
- Helps junior developers learn best practices.
- Can introduce security risks if not reviewed carefully.
While not a replacement for human developers, AI assistants boost productivity significantly.
Automated Testing and Bug Detection
AI-driven testing tools can predict where bugs are likely to occur and generate test cases automatically.
- Selenium with AI plugins can adapt test scripts dynamically.
- Tools like Testim.io use machine learning to stabilize flaky tests.
- Static code analyzers (e.g., SonarQube) detect vulnerabilities early.
This reduces manual effort and improves test coverage.
Intelligent Project Management
AI is now being used to forecast project timelines, estimate workloads, and identify at-risk tasks.
- Tools like Forecast.app use AI to optimize resource allocation.
- Predictive analytics help managers adjust plans proactively.
- Natural language processing extracts insights from meeting notes and tickets.
These capabilities make system development more predictable and data-driven.
Best Practices for Successful System Development Projects
Following proven best practices can dramatically increase the chances of delivering a successful system.
Start with User-Centered Design
Always design with the end-user in mind. Conduct user research, create personas, and validate assumptions through prototypes.
- Use tools like Figma or Adobe XD for interactive mockups.
- Run usability tests before full-scale development.
- Apply principles from Don Norman’s Design of Everyday Things.
A system that’s intuitive and user-friendly will see higher adoption rates.
Embrace Modularity and Scalability
Build systems that can grow with demand. Use modular architectures like microservices to isolate components.
- Design APIs with versioning in mind.
- Use containerization (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes) for scalability.
- Plan for horizontal scaling from the start.
This future-proofs your system against changing business needs.
Prioritize Security from Day One
Security shouldn’t be an afterthought. Integrate secure coding practices, conduct regular audits, and follow frameworks like OWASP.
- Perform threat modeling during the design phase.
- Use encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC).
Visit OWASP.org for free resources on application security.
Document Everything
Comprehensive documentation ensures knowledge transfer, supports maintenance, and aids onboarding.
- Maintain up-to-date API docs (e.g., with Swagger/OpenAPI).
- Write clear README files and architecture decision records (ADRs).
- Use wikis or internal knowledge bases.
Good documentation saves countless hours down the line.
Future Trends Shaping System Development
The field of system development is constantly evolving. Staying ahead requires awareness of emerging trends and technologies.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
These platforms allow non-developers to build applications using visual interfaces and drag-and-drop tools.
- Examples: Microsoft Power Apps, Bubble, OutSystems.
- Speeds up prototyping and internal tool development.
- May limit customization and scalability for complex systems.
They democratize system development, enabling citizen developers to contribute.
Cloud-Native Development
Building applications specifically for cloud environments (AWS, Azure, GCP) offers unmatched flexibility and resilience.
- Leverage serverless computing (e.g., AWS Lambda).
- Use managed services for databases, messaging, and authentication.
- Adopt Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with tools like Terraform.
Cloud-native apps are designed to be scalable, fault-tolerant, and easy to update.
Quantum Computing and Beyond
While still in early stages, quantum computing could revolutionize system development by solving problems intractable for classical computers.
- Potential applications: cryptography, optimization, drug discovery.
- Companies like IBM and Google are investing heavily.
- New programming models (e.g., Qiskit) are emerging.
Though not mainstream yet, developers should monitor this space for future opportunities.
What is system development?
System development is the process of creating, designing, testing, and maintaining software systems to meet specific business or user needs. It involves multiple phases, including planning, analysis, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
What are the main SDLC models?
The main SDLC models include Waterfall (sequential), Agile (iterative), Spiral (risk-focused), V-Model (testing emphasis), and DevOps (continuous integration and delivery). Each has its strengths depending on project scope and requirements.
How long does system development take?
Duration varies widely—from a few weeks for small apps to several years for large enterprise systems. Factors include project complexity, team size, methodology used, and stakeholder involvement.
Is coding required in system development?
Traditionally, yes—coding is a core part of implementation. However, with the rise of low-code/no-code platforms, some systems can be built with minimal or no hand-coding, especially for internal tools or simple applications.
What skills are needed for system development?
Key skills include programming, problem-solving, database design, system analysis, project management, and communication. Familiarity with SDLC methodologies, version control, and testing tools is also essential.
System development is a dynamic and multifaceted discipline that sits at the heart of digital innovation. From defining requirements to maintaining live systems, every phase plays a crucial role in delivering value. By choosing the right methodology, leveraging modern tools, and following best practices, teams can build robust, scalable, and user-centric systems. As AI, cloud computing, and low-code platforms reshape the landscape, staying adaptable and informed will be key to long-term success in this ever-evolving field.
Further Reading: